本文主要介绍通过CNN+DQN模型来实现玩AI玩FlappyBird。
介绍
今天主要介绍如何通过强化学习来让程序玩FlappyBird。
最终的效果如下:
上面的效果实在进行了2000000次迭代训练之后得到的结果。几乎已经可以碾压人类玩家了。
算法
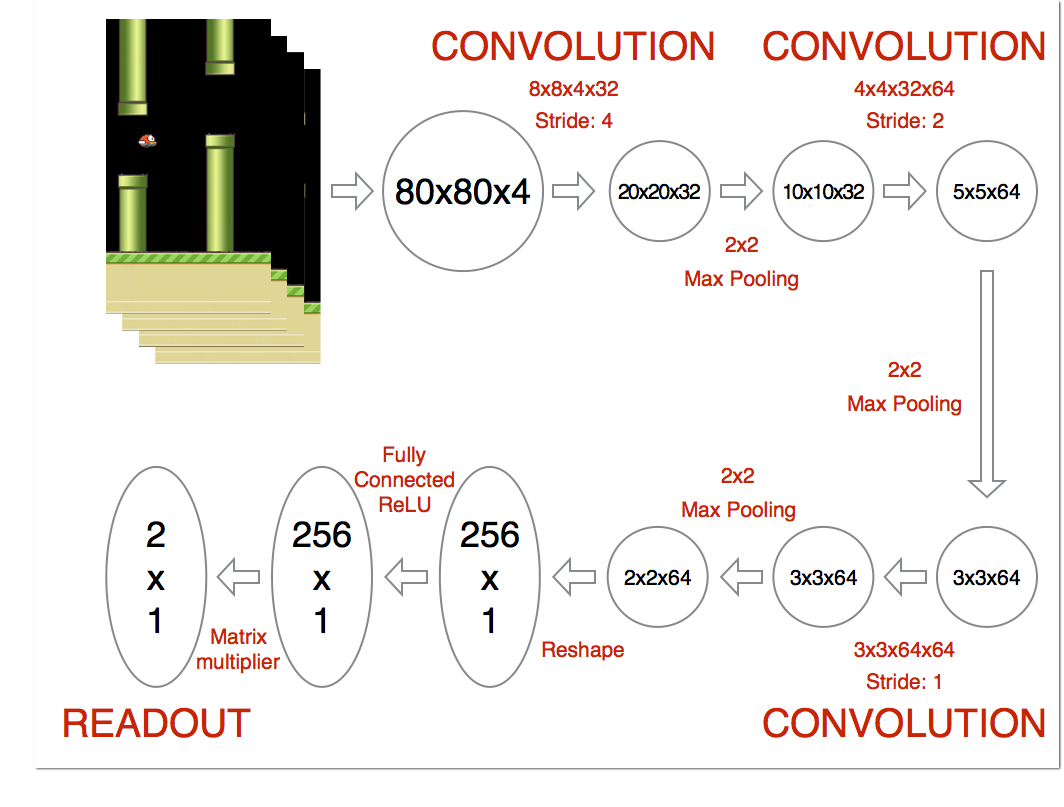
整体的算法是CNN+DQN,并通过奖励值对网络进行训练。模型的整体结构如下图。
具体CNN和DQN算法的原理可以参考之前写过的文章,这里重点介绍模型的代码实现。
实现
游戏环境的实现就不具体解释了,没什么太难得地方,了解Pygame模块之后,程序没有太难的地方。
重点来看一下神经网络的搭建以及训练的过程。
代码用到的主要模块及版本:
Python:3.5.3
TensorFlow:1.0.1
cv2:3.3.0
pygame:1.9.3
首先是一些超参数的设置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| ACTIONS = 2 GAMMA = 0.99 OBSERVE = 100000. EXPLORE = 2000000. FINAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 INITIAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 REPLAY_MEMORY = 50000 BATCH = 32 FRAME_PER_ACTION = 1
|
然后是神将网络的搭建:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53
| def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev = 0.01) return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.01, shape = shape) return tf.Variable(initial) def conv2d(x, W, stride): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides = [1, stride, stride, 1], padding = "SAME") def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize = [1, 2, 2, 1], strides = [1, 2, 2, 1], padding = "SAME") def createNetwork(): W_conv1 = weight_variable([8, 8, 4, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) W_conv2 = weight_variable([4, 4, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) W_conv3 = weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64]) b_conv3 = bias_variable([64]) W_fc1 = weight_variable([1600, 512]) b_fc1 = bias_variable([512]) W_fc2 = weight_variable([512, ACTIONS]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([ACTIONS]) s = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 80, 80, 4]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(s, W_conv1, 4) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2, 2) + b_conv2) h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_conv2, W_conv3, 1) + b_conv3) h_conv3_flat = tf.reshape(h_conv3, [-1, 1600]) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_conv3_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) readout = tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2 return s, readout, h_fc1
|
神经网络一共3个卷基层和2个全连接层。
最终代码里的实现结构和上面图中的结构有一些差别,输入图片大小为80x80x4。第一个卷基层得到图片的尺寸为20x20x32,然后加一个maxpooling层,得到10x10x32的图片。第二个卷基层得到的图片尺寸为10x10x64。第三个卷基层得到图片的尺寸为5x5x64。然后将得到的数据产开,得到1600x1的数据,然后经过第一个全连接层得到512x1的数据,然后经过第二个全连接层最终得到对应的动作值。
然后计算损失函数和优化规则:
1 2 3
| readout_action = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(readout, a), reduction_indices=1) cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - readout_action)) train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-6).minimize(cost)
|
然后根据动作得到当前的图片,并对图片进行裁剪:
1 2 3 4 5
| do_nothing = np.zeros(ACTIONS) do_nothing[0] = 1 x_t, r_0, terminal = game_state.frame_step(do_nothing) x_t = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(x_t, (80, 80)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret, x_t = cv2.threshold(x_t,1,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
|
代码中cv2.resize()将图片尺寸转化成80x80,cv2.cvtColor()对图像进行灰度化,cv2.threshold()将图像二值化。
然后导入保存好的网络参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| saver = tf.train.Saver() sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) checkpoint = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state("saved_networks") if checkpoint and checkpoint.model_checkpoint_path: saver.restore(sess, checkpoint.model_checkpoint_path) print("Successfully loaded:", checkpoint.model_checkpoint_path) else: print("Could not find old network weights")
|
然后根据当前的状态图片得到对应的动作,并通过概率判断是否选择最优动作或进行探索。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
| readout_t = readout.eval(feed_dict={s : [s_t]})[0] a_t = np.zeros([ACTIONS]) action_index = 0 if t % FRAME_PER_ACTION == 0: if random.random() <= epsilon: print("----------Random Action----------") action_index = random.randrange(ACTIONS) a_t[random.randrange(ACTIONS)] = 1 else: action_index = np.argmax(readout_t) a_t[action_index] = 1 else: a_t[0] = 1
|
将动作值输入游戏环境总得到奖励值,和下一步的状态值图片,并对下一步的状态图片进行裁剪。并保存当前状态,动作值,奖励值和下一步状态。如果存储空间的大小大于存储的大小,则删除之前的数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| x_t1_colored, r_t, terminal = game_state.frame_step(a_t) x_t1 = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(x_t1_colored, (80, 80)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret, x_t1 = cv2.threshold(x_t1, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) x_t1 = np.reshape(x_t1, (80, 80, 1)) s_t1 = np.append(x_t1, s_t[:, :, :3], axis=2) D.append((s_t, a_t, r_t, s_t1, terminal)) if len(D) > REPLAY_MEMORY: D.popleft()
|
从存储的数据中采样mimibatch大小的数据对网络进行训练,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
| minibatch = random.sample(D, BATCH) s_j_batch = [d[0] for d in minibatch] a_batch = [d[1] for d in minibatch] r_batch = [d[2] for d in minibatch] s_j1_batch = [d[3] for d in minibatch] y_batch = [] readout_j1_batch = readout.eval(feed_dict = {s : s_j1_batch}) for i in range(0, len(minibatch)): terminal = minibatch[i][4] if terminal: y_batch.append(r_batch[i]) else: y_batch.append(r_batch[i] + GAMMA * np.max(readout_j1_batch[i])) train_step.run(feed_dict = { y : y_batch, a : a_batch, s : s_j_batch} )
|
以上就是主要的代码片段。运行程序,导入现有的网络参数就可以看到上面的游戏效果。
参考资料: